Im Englischen drückt das Past Perfect die Vorvergangenheit aus. Warum das eine wichtige Zeitform ist, wann du sie benutzt und wie du sie bildest, erfährst du hier. Außerdem lernst du, wo Stolperfallen und Verwechslungsgefahr lauern.
Bildung des Past Perfect
Die Bildung des Past Perfect auf einen Blick
Die Bildung des Past Perfect Simple besteht bei allen Personen, egal ob Singular oder Plural, aus:
1️⃣ had +
2️⃣ Past Participle des Verbs.
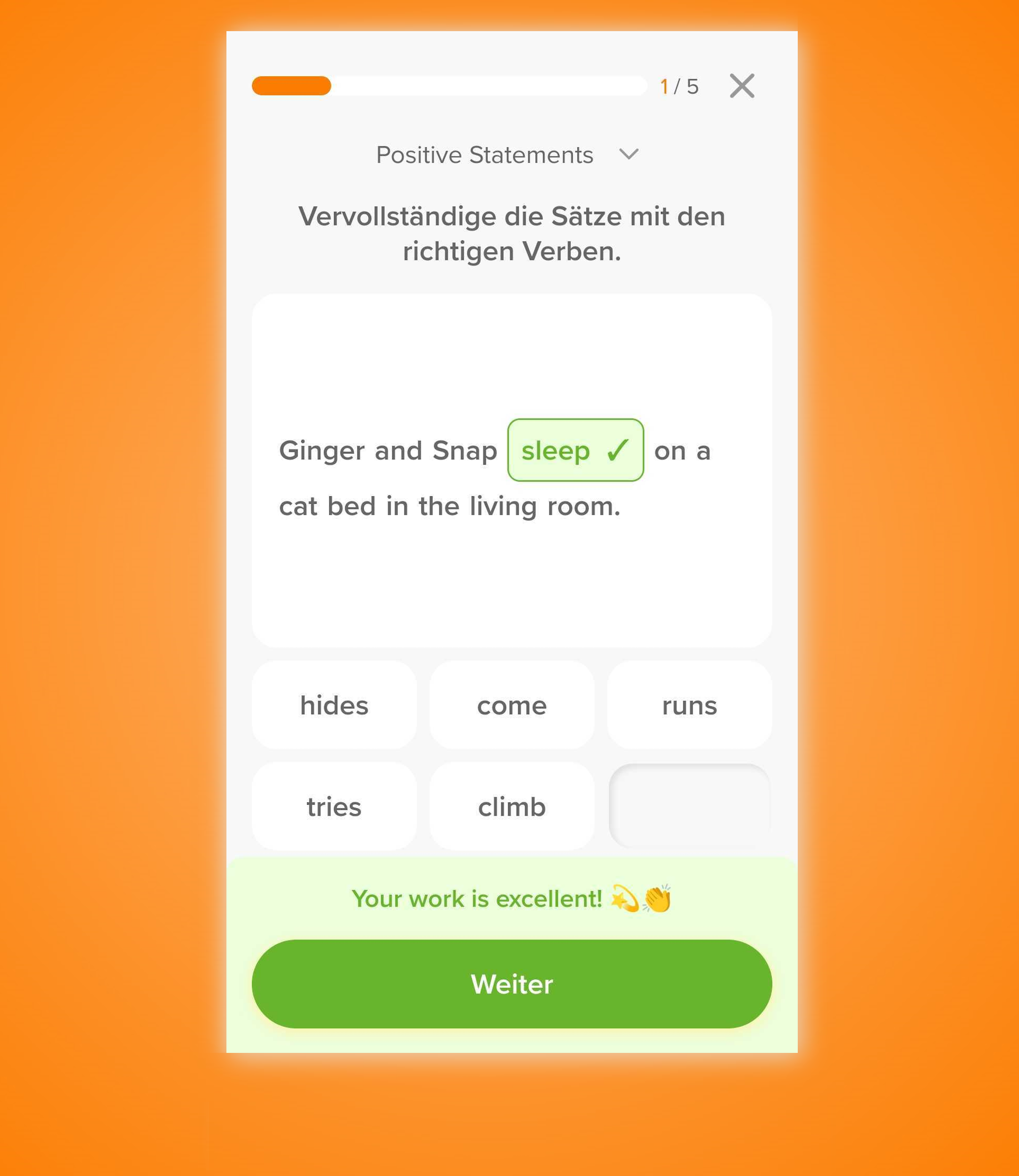
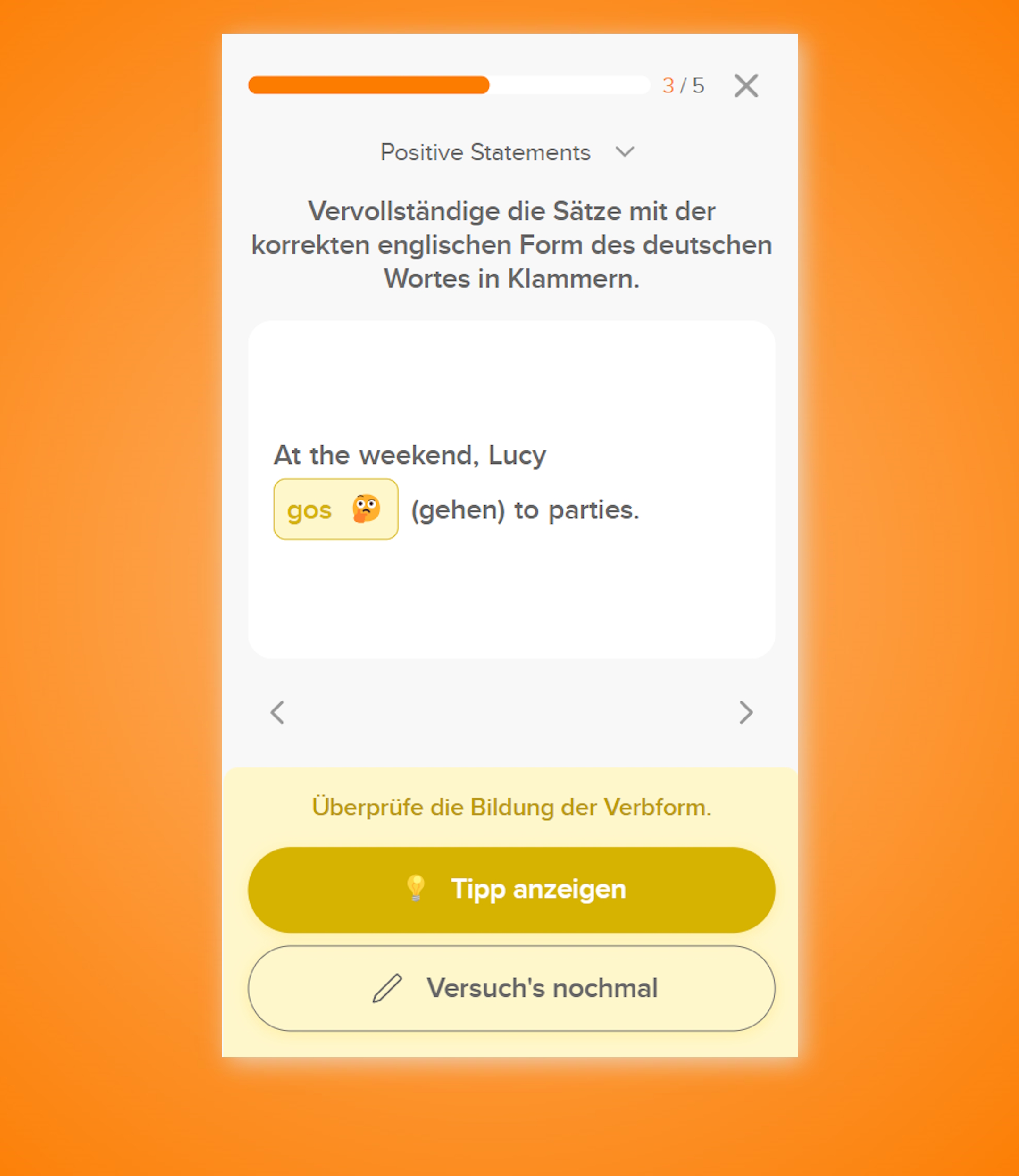
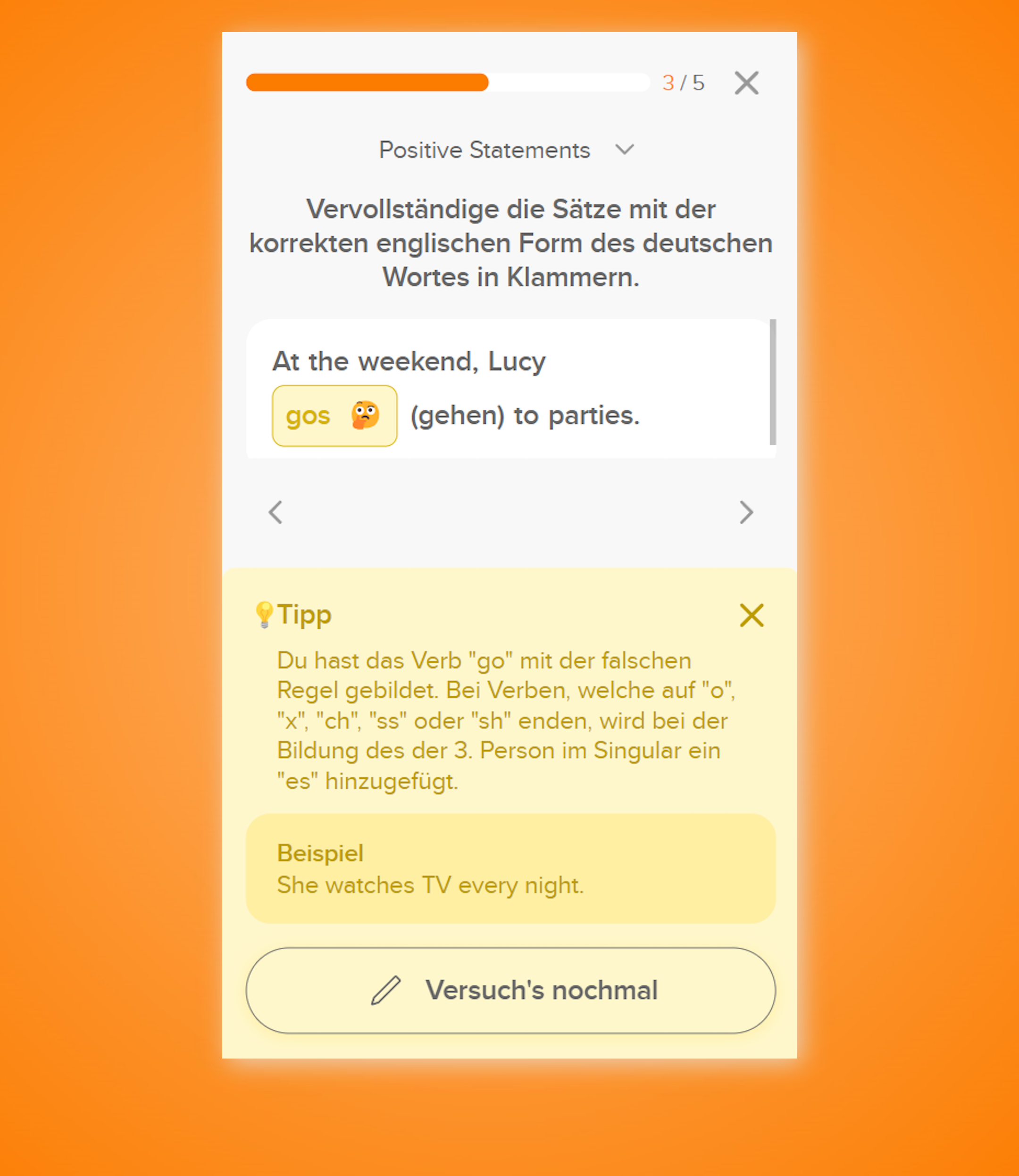
Das Past Participle wird bei regelmäßigen Verben gebildet, indem du –ed an die Infinitiv-Form anhängst.
» He had (1️⃣) done (2️⃣) his homework. «
Beispiele (allgemein)
| Infinitiv | Deutsch | Past Participle | Past Perfect |
| to walk | gehen | walked | had walked |
| to call | rufen | called | had called |
| to answer | antworten | answered | had answered |
Beispiele (Endung -e, -y & Konsonant+ kurzer Vokal)
- Endet das Verb bereits auf -e, dann hängst du nur nach das -d an.
- Endet das Verb auf –y, dann wird im Past Participle daraus –ie und du hängst ein -d an.
- Endet das Verb auf einen Konsonanten, der auf einen kurzen Vokal folgt, wird der Konsonant verdoppelt.
| Infinitiv | Deutsch | Past Participle | Past Perfect |
| to move | bewegen | moved | had moved |
| to try | versuchen | tried | had tried |
| to hug | umarmen | hugged | had hugged |
Beispiele (unregelmäßige Verben)
Es gibt außerdem eine ganze Reihe unregelmäßiger Verben. Bei denen musst du das Past Participle einfach lernen.
| Infinitiv | Deutsch | Past Participle | Past Perfect |
| to be | sein | been | had been |
| to run | laufen | run | had run |
| to think | denken | thought | had thought |
| to take | nehmen | taken | had taken |
Kurzform: Achtung Verwechslungsgefahr!
👉 Du kannst had auch mit ’d abkürzen.
Aber Vorsicht: Auch das Verb would kann so abgekürzt werden. Hier besteht also Verwechslungsgefahr!
Beispiele:
- I had/I’d run away when he arrived. – Ich war weggelaufen, als er ankam.
- I would/I’d run away when he arrives. – Ich würde weglaufen, wenn er ankommt.
Past Perfect Übungen:
- After she had finished (to finish) her homework, she went out to play.
- By the time we arrived, the movie had already started (to start).
- He didn’t eat the sandwich because he had had (to have) lunch already.
- They had visited (to visit) the museum before they went to the park.
- She had never seen (to see) a lion before she went to the zoo.
- After we had cleaned (to clean) the house, we were very tired.
- He had saved (to save) enough money before he bought the car.
- By the time she called, I had already left (to leave).
- We didn’t understand the story because we hadn’t read (to read) the book.
- After they had packed (to pack) their bags, they went to the airport.
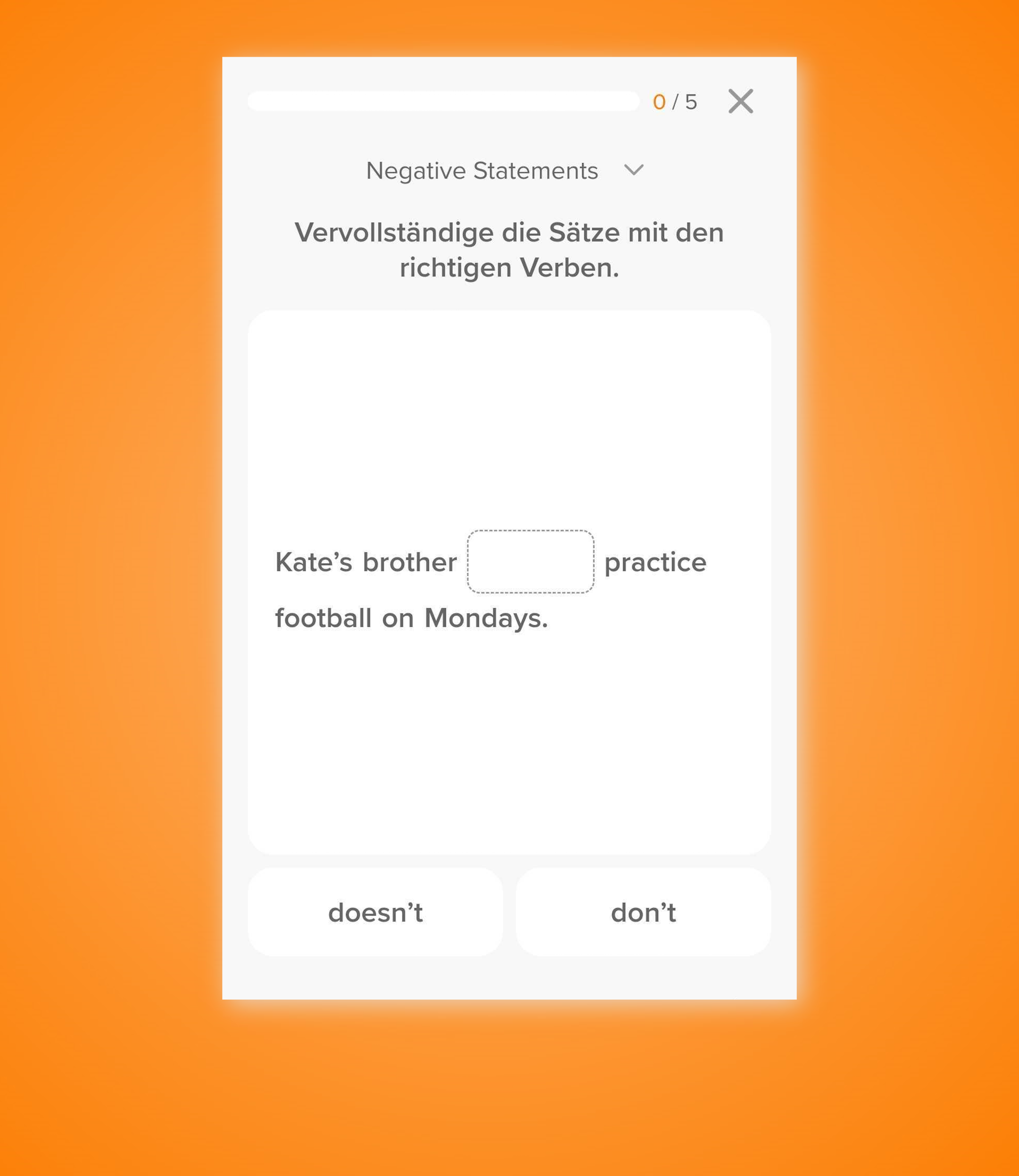
Verneinung & Fragen im Past Perfect
❌ Wenn du Aussagen im Past Perfect verneinen willst, gehst du wie folgt vor:
Option 1️⃣
Du fügst nach had das Wort not ein.
➡️ Although I had not studied I passed my exam. – Obwohl ich nicht gelernt hatte, bestand ich meine Prüfung.
Option 2️⃣
Alternativ kannst du auch die Kurzform benutzen, bei der du had not zu hadn’t zusammenziehst.
➡️ Although I hadn’t studied I passed my exam. – Obwohl ich nicht gelernt hatte, bestand ich meine Prüfung.
❓Bei Fragen ändert sich die Wortstellung im Satz:
Das had rückt vor das Subjekt, dann folgt das Verb.
➡️ Had you finished your food before it got cold? – Hattest du dein Essen beendet, bevor es kalt wurde?
Wann benutzt man Past Perfect?
Wenn du etwas erzählst, ist es wichtig, dass dein Gegenüber die Reihenfolge der Ereignisse versteht. Darum gibt es in vielen Sprachen Zeitformen, die ausdrücken, dass etwas vor einer Sache passiert ist, die ebenfalls bereits vorbei ist.
Im Deutschen erfüllt das Plusquamperfekt diese Aufgabe. Im Englischen heißt die Form der Vorvergangenheit Past Perfect oder Past Perfect Simple.
Past Perfect allein im Satz
Seltener kann Past Perfect Simple auch allein im Satz stehen. Das kommt vor, wenn ein abgeschlossenes Ereignis in der Vergangenheit stattgefunden hat und keinen Einfluss mehr auf die Gegenwart oder Zukunft hat.
Past Perfect mit Simple Past
Past Perfect in if-clauses
Häufiger begegnet dir die Vorvergangenheit in if-clauses (Konditionalsätzen) des 3. Typs. Sie drücken Bedingungen aus, die nicht mehr erfüllt werden können, weil die Ereignisse schon vorbei sind. Dabei steht der if–Satz im Past Perfect, der Hauptsatz im Conditional II.
Signalwörter für die Verwendung des Past Perfect
Du machst Übersetzungen oder Übungen und weißt nicht genau, ob Past Perfect die richtige Wahl ist? Dann können Signalwörter dir helfen.
⚠️ Aber Vorsicht: Ein Signalwort bedeutet nicht, dass hier immer Past Perfect angebracht ist, sie sind aber ein guter Hinweis.
| Englisch | Deutsch |
| when | als |
| before | bevor |
| after | nachdem |
| once | einst/früher |
| already | bereits |
| just | gerade eben |
| never | nie |
| until | bis |
| as soon as | sobald/als |
| because | weil |
| although | obwohl |
Gemischte Past Perfect Übungen:
Hier haben wir für dich noch eine gemischte Übung, mit allen bisher gelernten Varianten des Past Perfect, zusammengestellt. 🤓
- If I had known (to know) that, I wouldn’t have acted like this.
- Had they eaten (to eat) dinner before they left (to leave) the house?
- Tom had bought (to buy) a book.
- She didn’t go (to go) to the party because she had not been invited (to not invite).
- Before he watched (to watch) the movie, he had read (to read) the book.
- Had you seen (to see) that movie before?
- If she had seen (to see) the sign, she wouldn’t have made a wrong turn.
- They had finished (to finish) their homework.
- Once we had finished (to finish) our project, we went (to go) for a walk.
- We had not cleaned (to clean) the house before the guests arrived.
- After they had repaired (to repair) the car, they finally left (to leave).
- If I hadn’t missed (to miss) the bus, I would have been on time.
- Had she gone (to go) to the store before it closed?
- By the time I got (to get) to the station, the train had already departed (to depart).
- They had lived (to live) in London before they moved (to move) to New York.
- If we had prepared (to prepare) better, we would have won the game.
- He had saved (to save) enough money before he bought (to buy) the car.
- She had never seen (to see) a lion before she went (to go) to the zoo.
- If you hadn’t been (to be) late, we wouldn’t have missed the movie.
- Had he read (to read) the book before the class?
Fast perfekt im Past Perfect und phase6
Bei den Zeitformen heißt es nicht nur wegen der unregelmäßigen Verben: üben, üben, üben. Damit du das immer & überall tun kannst, gibt es den phase6 Grammatiktrainer. Hier findest du im Handumdrehen alle wichtigen Regeln zu jeder Zeitform. Dazu gibt es jede Menge Übungen, abgestimmt auf deine Lehrbücher.